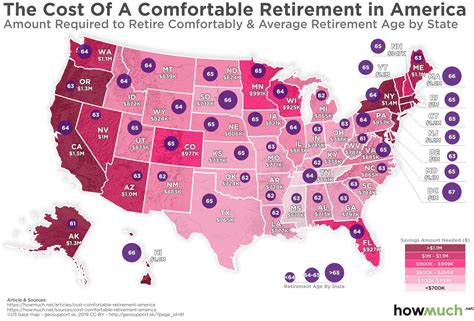
A comfortable retirement now requires $1.47 million, yet a staggering 97% of Americans are projected to fall short of this target by 2025, according to a recent analysis by Principal Financial Group. This alarming statistic underscores the growing retirement crisis facing Americans, fueled by inflation, market volatility, and inadequate savings.
The Principal Financial Group’s Retirement Security Barometer, cited in the original Yahoo Finance article, reveals the substantial gap between the desired retirement nest egg and the reality for most individuals. The $1.47 million benchmark represents the amount needed to maintain a pre-retirement standard of living, considering factors like healthcare costs, housing, and everyday expenses. The study highlights that even those actively saving for retirement face significant challenges in reaching this ambitious goal.
“Many Americans are facing headwinds in their retirement savings journey,” said an analyst from Principal Financial Group. “Inflation, market fluctuations, and unexpected expenses can all derail even the most well-intentioned savers.”
The reasons behind this widespread shortfall are multifaceted. Stagnant wages, coupled with rising living costs, leave many individuals with little disposable income to allocate to retirement savings. Furthermore, the shift from traditional pension plans to 401(k)s and other defined contribution plans has placed greater responsibility on individuals to manage their own retirement investments, a task that requires financial literacy and discipline. The lack of access to financial education and professional advice further exacerbates the problem, particularly for low- and middle-income earners.
The implications of this looming retirement crisis are far-reaching. As more Americans enter retirement without adequate savings, they risk facing financial hardship, relying on government assistance, or delaying retirement altogether. This, in turn, can strain social safety nets and create workforce shortages.
Diving Deeper into the Retirement Savings Gap
The $1.47 million figure, while daunting, provides a crucial benchmark for understanding the scope of the retirement savings challenge. However, it is important to recognize that this number is an average and individual retirement needs can vary significantly based on factors such as lifestyle, health status, and geographic location.
To better understand the retirement savings gap, it’s essential to consider the various components that contribute to a comfortable retirement. These include:
- Basic Living Expenses: Housing, food, transportation, and utilities form the foundation of retirement expenses. These costs can vary widely depending on location and lifestyle choices.
- Healthcare Costs: Healthcare expenses are a major concern for retirees, particularly as they age. Medicare covers some healthcare costs, but it doesn’t cover everything. Supplemental insurance and out-of-pocket expenses can significantly impact retirement savings.
- Leisure and Recreation: Retirement is often envisioned as a time for travel, hobbies, and other leisure activities. These activities require financial resources, and it’s important to factor them into retirement planning.
- Inflation: Inflation erodes the purchasing power of savings over time. It’s crucial to account for inflation when estimating retirement expenses.
- Taxes: Retirement income is typically subject to taxes. It’s important to understand the tax implications of different retirement income sources.
Factors Contributing to the Retirement Savings Crisis
Several factors have contributed to the growing retirement savings crisis in America:
- Stagnant Wages: Wage growth has lagged behind inflation for decades, making it difficult for many Americans to save for retirement.
- Rising Living Costs: The cost of housing, healthcare, education, and other essential goods and services has increased significantly in recent years, further straining household budgets.
- Shift to Defined Contribution Plans: The shift from traditional pension plans to 401(k)s and other defined contribution plans has shifted the responsibility for retirement savings from employers to employees.
- Lack of Financial Literacy: Many Americans lack the financial literacy skills needed to effectively manage their retirement savings.
- Debt Burden: High levels of debt, including student loans, mortgages, and credit card debt, can make it difficult to save for retirement.
- Unexpected Expenses: Unexpected expenses, such as medical bills or job loss, can derail even the most well-intentioned retirement savers.
- Market Volatility: Market volatility can erode retirement savings, particularly for those nearing retirement.
Strategies to Improve Retirement Savings
Despite the challenges, there are several strategies that individuals can use to improve their retirement savings:
- Start Saving Early: The earlier you start saving, the more time your money has to grow.
- Contribute Regularly: Make regular contributions to your retirement accounts, even if it’s a small amount.
- Take Advantage of Employer Matching: If your employer offers a 401(k) match, take full advantage of it. This is essentially free money.
- Increase Contributions Over Time: As your income increases, increase your retirement contributions.
- Diversify Investments: Diversify your investments to reduce risk.
- Seek Professional Advice: Consider seeking professional advice from a financial advisor.
- Reduce Debt: Reducing debt can free up more money for retirement savings.
- Create a Budget: Creating a budget can help you track your spending and identify areas where you can save money.
- Automate Savings: Automate your savings to make it easier to save regularly.
- Consider Delaying Retirement: Delaying retirement can give you more time to save and allow your investments to grow.
- Work Part-Time in Retirement: Working part-time in retirement can provide additional income and help you stretch your savings.
- Downsize Your Home: Downsizing your home can free up equity that can be used to supplement your retirement income.
Government and Employer Initiatives
Addressing the retirement savings crisis requires a multi-pronged approach involving individuals, employers, and the government. Some potential solutions include:
- Expanding Access to Retirement Savings Plans: Expanding access to retirement savings plans, particularly for small businesses and low-income workers.
- Increasing the Saver’s Credit: Increasing the Saver’s Credit, a tax credit for low- and moderate-income individuals who save for retirement.
- Strengthening Social Security: Strengthening Social Security to ensure its long-term solvency.
- Promoting Financial Literacy: Promoting financial literacy education in schools and workplaces.
- Encouraging Employer Matching: Encouraging employers to offer generous 401(k) matching contributions.
- Creating Automatic Enrollment Programs: Creating automatic enrollment programs in 401(k) plans.
The Role of Financial Advisors
Financial advisors can play a crucial role in helping individuals plan for retirement. They can provide personalized advice on:
- Retirement Planning: Helping individuals develop a comprehensive retirement plan.
- Investment Management: Managing investments to help individuals reach their retirement goals.
- Tax Planning: Minimizing taxes in retirement.
- Estate Planning: Planning for the transfer of assets to heirs.
- Insurance Planning: Ensuring adequate insurance coverage in retirement.
The Impact of Inflation on Retirement Savings
Inflation is a significant threat to retirement savings. Even modest inflation rates can erode the purchasing power of savings over time. For example, if inflation averages 3% per year, the purchasing power of $1 million will be reduced by almost 50% over 25 years.
To protect against inflation, it’s important to invest in assets that are likely to outpace inflation, such as stocks, real estate, and commodities. Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS) are another option.
The Importance of Long-Term Care Planning
Long-term care expenses can be substantial and can significantly deplete retirement savings. It’s important to plan for long-term care needs, either through long-term care insurance or by setting aside funds specifically for this purpose.
The Psychological Impact of Retirement Planning
Retirement planning is not just about numbers. It’s also about psychology. Many people find it difficult to think about retirement, either because they are afraid of getting old or because they don’t want to face the reality that they may not have enough money to retire comfortably.
It’s important to address these psychological barriers to retirement planning. Talking to a financial advisor or a therapist can be helpful.
The Future of Retirement
The future of retirement is uncertain. Several factors, such as technological advancements, demographic shifts, and economic changes, could impact retirement in the years to come.
It’s important to stay informed about these trends and to adapt your retirement plan accordingly.
The Silver Lining: It’s Not Too Late
While the statistics paint a concerning picture, it’s important to remember that it’s not too late to take action and improve your retirement prospects. Even small changes to your savings habits can make a big difference over time. The key is to start now and to stay committed to your retirement goals.
Expanding on the Principal Financial Group’s Findings
The Principal Financial Group’s research isn’t just a standalone observation. It echoes similar findings from other financial institutions and research organizations. These studies consistently point to a growing gap between what Americans need to retire comfortably and what they’ve actually saved. This convergence of data reinforces the severity of the retirement crisis and underscores the need for urgent action.
One key takeaway from the Principal study is the importance of proactive planning. The report likely delves into the behaviors and strategies of those who are on track to meet their retirement goals, providing valuable insights for others. This could include information on asset allocation, savings rates, and the use of financial planning tools. Understanding these successful strategies can empower individuals to take control of their retirement planning and increase their chances of achieving financial security in their later years.
Moreover, the Principal report likely explores the demographic disparities in retirement savings. Factors such as age, income, education, and gender can all influence an individual’s ability to save for retirement. Understanding these disparities is crucial for developing targeted solutions that address the unique needs of different populations. For example, programs that provide financial literacy education to underserved communities can help close the retirement savings gap.
The Impact on Future Generations
The current retirement crisis has significant implications for future generations. As more Americans retire without adequate savings, they may be forced to rely on government assistance, which could strain social safety nets. This could lead to higher taxes and reduced benefits for future generations.
Furthermore, the financial burden of caring for aging parents could fall on the shoulders of their children, further exacerbating the financial challenges facing younger generations. It’s crucial to address the retirement savings crisis now to prevent it from becoming an even bigger problem in the future.
Beyond the Numbers: The Human Cost
While the numbers provide a stark overview of the retirement savings crisis, it’s important to remember that behind each statistic is a real person with hopes, dreams, and anxieties about the future. The prospect of retiring without adequate savings can be incredibly stressful and can impact an individual’s mental and physical health.
The lack of financial security in retirement can lead to difficult choices, such as delaying medical care, cutting back on essential expenses, or relying on family members for support. It can also limit opportunities for travel, hobbies, and other activities that can enrich retirement years.
Addressing the retirement savings crisis is not just about numbers; it’s about ensuring that all Americans have the opportunity to retire with dignity and security.
Conclusion
The Principal Financial Group’s finding that 97% of Americans are projected to fall short of a comfortable retirement by 2025 serves as a wake-up call. The challenges are significant, but not insurmountable. By taking proactive steps to improve their savings habits, seeking professional advice, and advocating for policies that promote retirement security, individuals can increase their chances of achieving a comfortable and fulfilling retirement. The collaboration of individuals, employers, and the government is essential to mitigate the looming retirement crisis and ensure a more secure future for all Americans.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How much money do I actually need to retire comfortably?
The widely cited $1.47 million figure from Principal Financial Group is an average. Your individual retirement needs depend on several factors, including your desired lifestyle, health status, location, and anticipated expenses. A more accurate estimate requires a detailed assessment of your personal circumstances. Consider using online retirement calculators, consulting with a financial advisor, and carefully projecting your future expenses. Factors to consider are housing costs (will you have a mortgage or rent?), healthcare costs (including potential long-term care), food, transportation, leisure activities, and inflation. Many financial planners suggest aiming to replace 70-80% of your pre-retirement income.
2. What are the biggest factors contributing to the retirement savings shortfall?
Several factors contribute to the retirement savings shortfall. These include:
- Stagnant Wages: Wage growth hasn’t kept pace with inflation.
- Rising Living Costs: Housing, healthcare, and education costs have increased substantially.
- Shift to Defined Contribution Plans: Responsibility for retirement savings has shifted from employers to employees with 401(k)s.
- Lack of Financial Literacy: Many people lack the knowledge to manage their retirement savings effectively.
- Debt Burden: High levels of debt make saving difficult.
- Unexpected Expenses: Unforeseen expenses can derail savings plans.
- Market Volatility: Market fluctuations can erode savings, especially nearing retirement.
- Inflation: The most recent surge in inflation has severely impacted people’s savings.
3. What can I do now to improve my retirement savings, even if I’m starting late?
Even if you’re starting late, several strategies can help:
- Increase Savings Rate: Aggressively increase your savings contributions. Even small increases can make a significant difference over time.
- Take Advantage of Employer Matching: Maximize employer 401(k) matching contributions – it’s free money.
- Consolidate Debt: Reduce high-interest debt to free up cash flow for savings.
- Delay Retirement: Working a few extra years allows you to save more and potentially delay drawing on your retirement funds.
- Downsize Expenses: Identify areas where you can cut back on spending and redirect those funds to savings.
- Seek Professional Advice: A financial advisor can help you develop a personalized retirement plan and investment strategy.
- Consider a Roth IRA/401(k): Depending on your current and anticipated future tax bracket, a Roth IRA or Roth 401(k) could offer tax advantages in retirement.
4. How does inflation impact my retirement savings, and what can I do about it?
Inflation erodes the purchasing power of your savings. To mitigate its impact:
- Invest in Inflation-Resistant Assets: Consider investing in assets that tend to outpace inflation, such as stocks, real estate, and Treasury Inflation-Protected Securities (TIPS).
- Adjust Retirement Projections: Factor in realistic inflation rates when estimating your future expenses.
- Re-evaluate Spending Plans: Be prepared to adjust your spending habits in retirement to account for rising costs.
- Consider Delaying Social Security: Delaying Social Security benefits can result in a larger monthly payment, which can help offset the effects of inflation.
- Work Longer: Remaining in the workforce longer, even part-time, allows you to defer drawing down retirement savings and potentially increase your income.
5. What role does Social Security play in retirement, and will it be enough?
Social Security is a crucial part of retirement income for many Americans, but it is generally not sufficient to cover all retirement expenses. Social Security was designed to replace about 40% of pre-retirement income for average earners. The exact amount you receive depends on your earnings history and the age at which you begin claiming benefits.
Given the projected retirement savings shortfall, it’s essential to view Social Security as a supplement to, rather than a replacement for, personal savings and other retirement income sources. Furthermore, the future of Social Security is uncertain, with potential benefit reductions or changes to eligibility requirements looming. Relying solely on Social Security is a risky retirement strategy.