After five years of solar panel installation, a homeowner’s energy bill plummeted to a mere $45, a stark contrast to previous hefty expenses, showcasing the long-term financial benefits of renewable energy investments.
A Colorado homeowner’s recent social media post detailing their dramatically reduced energy bill after five years with solar panels has sparked widespread interest in residential solar energy. The homeowner, identified as Reddit user u/Technicolor_Sunset, shared an image of their monthly energy bill, revealing a total charge of just $45. The post quickly went viral, garnering thousands of upvotes and comments from individuals considering or already invested in solar energy solutions. This story underscores the potential for significant long-term cost savings and environmental benefits associated with solar panel adoption.
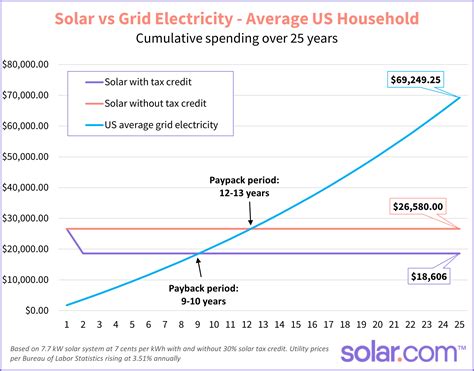
The initial investment in solar panels can be substantial, often ranging from $15,000 to $25,000 or more, depending on the size of the system and local installation costs. However, the financial returns can be considerable over the lifespan of the panels, which typically lasts 25 to 30 years. The primary benefit is a reduction in monthly energy bills, as solar panels generate electricity during daylight hours, offsetting the need to purchase power from the grid. In many cases, homeowners can even generate excess electricity, which is then sold back to the utility company through a process called net metering. This can result in credits on their energy bill or even cash payments.
According to u/Technicolor_Sunset, “We went solar in 2019. Best decision ever. My bill is just the connection fee and any overage.” This statement highlights a common scenario for solar panel owners: a base charge for remaining connected to the grid, ensuring power supply during nighttime or periods of low sunlight, coupled with charges for any electricity consumed beyond what the solar panels generate.
The financial advantages extend beyond reduced energy bills. Many states and the federal government offer incentives, such as tax credits and rebates, to encourage solar panel adoption. The federal solar tax credit, for example, allows homeowners to deduct a percentage of the cost of installing solar panels from their federal taxes. These incentives can significantly reduce the upfront cost of solar panel installation, making it a more attractive investment.
Furthermore, solar panels increase a home’s property value. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to sell for more than comparable homes without solar panels. Potential buyers are often willing to pay a premium for homes with solar panels because they recognize the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits.
The environmental benefits of solar energy are also significant. Solar panels generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases or air pollutants, reducing reliance on fossil fuels and mitigating the impacts of climate change. Solar energy is a clean, renewable energy source that can help to reduce carbon emissions and improve air quality. By investing in solar panels, homeowners can contribute to a more sustainable energy future.
The popularity of the Reddit post reflects a growing interest in solar energy as a viable alternative to traditional electricity sources. As technology improves and costs decrease, solar energy is becoming increasingly accessible to homeowners. Factors driving this trend include rising electricity prices, growing awareness of climate change, and government incentives that make solar panel installation more affordable.
However, potential solar panel adopters must consider several factors before making a decision. The amount of sunlight a home receives, the orientation and angle of the roof, and local building codes can all affect the performance of solar panels. It is crucial to conduct a thorough assessment of a home’s suitability for solar panels and to obtain quotes from multiple installers to ensure competitive pricing.
Moreover, the long-term maintenance of solar panels should be considered. While solar panels are generally durable and require minimal maintenance, they may need to be cleaned periodically to remove dirt and debris that can reduce their efficiency. Additionally, the inverters, which convert the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used in homes, may need to be replaced after 10 to 15 years. These maintenance costs should be factored into the overall financial analysis of solar panel adoption.
The experience of u/Technicolor_Sunset serves as a compelling case study for the potential benefits of solar energy. Their drastically reduced energy bill highlights the financial advantages of investing in renewable energy. As more homeowners share their positive experiences with solar panels, the technology is likely to become even more widespread, contributing to a cleaner and more sustainable energy future.
The homeowner’s post also brought attention to the importance of understanding net metering policies. Net metering allows homeowners to receive credit on their electricity bill for any excess electricity their solar panels send back to the grid. These policies vary by state and utility company, and understanding the specific rules in your area is crucial for maximizing the financial benefits of solar panels.
The increasing adoption of solar energy also has broader implications for the energy industry. As more homeowners generate their own electricity, the demand for traditional power sources decreases. This can lead to changes in the way utility companies operate and may require updates to the existing grid infrastructure to accommodate distributed energy generation.
In conclusion, the homeowner’s story underscores the potential for solar energy to transform the way we power our homes and communities. While the initial investment can be significant, the long-term financial and environmental benefits can be substantial. As technology continues to improve and costs continue to decline, solar energy is poised to play an increasingly important role in the transition to a cleaner, more sustainable energy future. The experience of u/Technicolor_Sunset provides a compelling example of the real-world benefits of solar energy and may inspire others to consider making the switch.
Expanding on the Factors Influencing Solar Panel Performance
Several factors play crucial roles in determining the efficiency and overall performance of solar panels. These encompass the amount of sunlight the panels receive, their orientation and angle, weather conditions, panel technology, and shading.
-
Sunlight Availability: The quantity of sunlight that solar panels receive is a fundamental factor. Regions with higher solar irradiance, measured in kilowatt-hours per square meter per day (kWh/m²/day), are more conducive to solar energy generation. Geographical location, seasonal changes, and daily weather patterns significantly impact sunlight availability. For example, areas closer to the equator generally receive more direct sunlight than those at higher latitudes. Cloud cover, fog, and smog can all reduce the amount of sunlight reaching the panels, thereby decreasing electricity production.
-
Orientation and Angle: The orientation of solar panels, referring to the direction they face (e.g., south, east, west), and their angle relative to the sun’s rays, substantially affect their performance. In the Northern Hemisphere, south-facing panels typically generate the most electricity because they receive the most direct sunlight throughout the day. The optimal angle of the panels depends on the latitude of the location. Generally, an angle close to the latitude is recommended. Some advanced solar panel systems include tracking mechanisms that automatically adjust the orientation and angle of the panels to maximize sunlight capture throughout the day.
-
Weather Conditions: Weather conditions, including temperature, precipitation, and cloud cover, have a direct impact on solar panel efficiency. While solar panels generate electricity from sunlight, high temperatures can actually decrease their efficiency. This is because the semiconductors in the panels operate more effectively at cooler temperatures. Precipitation, such as rain and snow, can help to clean the panels, removing dirt and debris that can reduce their performance. However, heavy snow accumulation can block sunlight and prevent electricity generation.
-
Panel Technology: The type of solar panel technology used also affects performance. The two primary types of solar panels are monocrystalline and polycrystalline. Monocrystalline panels are made from a single crystal of silicon and are generally more efficient than polycrystalline panels, which are made from multiple silicon crystals. Thin-film solar panels are another type of technology that is less efficient but can be more flexible and less expensive. Advances in solar panel technology continue to improve efficiency and reduce costs.
-
Shading: Shading from trees, buildings, or other obstructions can significantly reduce the amount of sunlight reaching solar panels, thereby decreasing their electricity production. Even partial shading can have a disproportionate impact on performance. Therefore, it is crucial to assess potential shading issues before installing solar panels and to take steps to minimize shading if possible. This may involve trimming trees or relocating the panels to a less shaded area.
Elaborating on Government Incentives and Policies
Government incentives and policies play a vital role in promoting the adoption of solar energy by making it more affordable and attractive for homeowners and businesses. These incentives can take various forms, including tax credits, rebates, grants, and net metering policies.
-
Federal Solar Tax Credit: One of the most significant incentives is the federal solar tax credit, also known as the Investment Tax Credit (ITC). This credit allows homeowners and businesses to deduct a percentage of the cost of installing solar panels from their federal taxes. The ITC has been instrumental in driving the growth of the solar industry in the United States. The credit has been extended and modified several times over the years, but it continues to provide a substantial financial incentive for solar energy adoption.
-
State and Local Incentives: In addition to the federal tax credit, many states and local governments offer their own incentives for solar energy. These incentives can include state tax credits, rebates, grants, and property tax exemptions. The specific incentives available vary widely from state to state and even within states. Some states have aggressive renewable energy goals and offer generous incentives to encourage solar energy adoption, while others have less developed incentive programs.
-
Net Metering Policies: Net metering is a policy that allows homeowners and businesses with solar panels to receive credit on their electricity bill for any excess electricity they send back to the grid. When solar panels generate more electricity than a home or business needs, the excess electricity is fed back into the grid, and the utility company credits the customer’s account. Net metering policies vary by state and utility company. Some states have mandatory net metering policies that require utilities to offer credit for excess electricity at the retail rate, while others have less favorable policies.
-
Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS): Renewable Portfolio Standards (RPS) are state laws that require utilities to generate a certain percentage of their electricity from renewable sources, such as solar, wind, and geothermal. RPS policies create a market for renewable energy and can drive investment in solar energy projects. Utilities often meet their RPS requirements by purchasing renewable energy credits (RECs) from solar energy producers.
-
Grants and Loan Programs: Some government agencies and non-profit organizations offer grants and loan programs to support solar energy projects. These programs can provide financial assistance to homeowners and businesses that may not be able to afford the upfront cost of solar panel installation. Grants typically do not need to be repaid, while loans offer financing at competitive interest rates.
Exploring the Impact on Property Value
The installation of solar panels can have a positive impact on a home’s property value. Studies have shown that homes with solar panels tend to sell for more than comparable homes without solar panels. This is because potential buyers recognize the long-term cost savings and environmental benefits associated with solar energy.
-
Increased Home Value: Several studies have examined the impact of solar panels on home values. These studies have generally found that homes with solar panels sell for a premium compared to similar homes without solar panels. The exact amount of the premium varies depending on factors such as the size of the solar panel system, the age of the system, and the location of the home. However, the overall trend is clear: solar panels can increase a home’s property value.
-
Attractiveness to Buyers: Homes with solar panels are often more attractive to potential buyers, particularly those who are environmentally conscious or who are looking for ways to reduce their energy bills. Solar panels can be a selling point for a home, highlighting its energy efficiency and sustainability. In some markets, homes with solar panels may even sell faster than comparable homes without solar panels.
-
Long-Term Savings: Potential buyers recognize that solar panels can provide long-term cost savings on their energy bills. This can make a home with solar panels more appealing than a home without solar panels. The amount of savings will depend on factors such as the size of the solar panel system, the amount of sunlight the home receives, and the local electricity rates. However, over the lifespan of the solar panels, the savings can be substantial.
-
Reduced Carbon Footprint: Some buyers are also attracted to homes with solar panels because they want to reduce their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. Solar panels generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, making them a clean and renewable energy source. Homes with solar panels can help buyers to live more sustainably and reduce their impact on the environment.
-
Market Demand: The impact of solar panels on property value can also depend on the local market demand for solar energy. In areas where solar energy is more popular, homes with solar panels may command a higher premium. Factors such as government incentives, environmental awareness, and local electricity rates can all influence the demand for solar energy.
Analyzing the Environmental Advantages of Solar Energy
Solar energy offers numerous environmental advantages compared to traditional fossil fuel-based energy sources. These advantages include reduced greenhouse gas emissions, improved air quality, and decreased reliance on finite resources.
-
Reduced Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Solar panels generate electricity without emitting greenhouse gases, such as carbon dioxide, methane, and nitrous oxide. These gases contribute to climate change by trapping heat in the atmosphere. By reducing greenhouse gas emissions, solar energy can help to mitigate the impacts of climate change, such as rising temperatures, sea-level rise, and extreme weather events.
-
Improved Air Quality: Solar panels also improve air quality by reducing the emission of air pollutants, such as sulfur dioxide, nitrogen oxides, and particulate matter. These pollutants can cause respiratory problems, cardiovascular disease, and other health issues. Fossil fuel-based power plants are a major source of air pollution, while solar panels generate electricity without emitting these harmful pollutants.
-
Decreased Reliance on Fossil Fuels: Solar energy reduces our reliance on fossil fuels, such as coal, oil, and natural gas. These resources are finite and non-renewable, meaning that they will eventually run out. Fossil fuels also have a significant environmental impact, from extraction and transportation to combustion and waste disposal. Solar energy is a renewable resource that can be harnessed indefinitely, reducing our dependence on fossil fuels and promoting energy independence.
-
Water Conservation: Solar energy can also help to conserve water. Fossil fuel-based power plants often require large amounts of water for cooling. This water is typically withdrawn from rivers, lakes, and other water bodies, which can have a negative impact on aquatic ecosystems. Solar panels do not require water for electricity generation, reducing the strain on water resources.
-
Land Use Considerations: While solar energy requires land for the installation of solar panels, the land use impacts can be minimized by siting solar projects on previously disturbed land, such as brownfields or landfills. Solar panels can also be installed on rooftops, reducing the need for land use. Additionally, solar energy can be combined with other land uses, such as agriculture, in a practice known as agrivoltaics.
Addressing Maintenance and Longevity of Solar Panels
The maintenance and longevity of solar panels are important considerations for homeowners and businesses considering solar energy. While solar panels are generally durable and require minimal maintenance, it is important to understand the maintenance requirements and expected lifespan of the panels.
-
Lifespan of Solar Panels: Solar panels typically have a lifespan of 25 to 30 years. This means that they will continue to generate electricity for at least 25 to 30 years, although their output may gradually decline over time. The performance of solar panels is typically warranted for a certain period, such as 25 years, with a guaranteed minimum output.
-
Maintenance Requirements: Solar panels require minimal maintenance. The primary maintenance task is to keep the panels clean to ensure that they are receiving maximum sunlight. Dirt, dust, pollen, and other debris can accumulate on the panels and reduce their efficiency. In most cases, rainfall will be sufficient to clean the panels. However, in areas with heavy dust or pollution, it may be necessary to clean the panels manually.
-
Inverter Replacement: The inverter is a critical component of a solar panel system that converts the direct current (DC) electricity generated by the panels into alternating current (AC) electricity used in homes and businesses. Inverters typically have a shorter lifespan than solar panels, often needing to be replaced after 10 to 15 years. The cost of inverter replacement should be factored into the overall cost of owning a solar panel system.
-
Monitoring and Inspections: It is important to monitor the performance of solar panels to ensure that they are operating efficiently. Many solar panel systems come with monitoring systems that allow homeowners to track their electricity generation and identify any potential problems. Regular inspections can also help to identify any issues, such as loose wiring or damaged panels.
-
Warranty Coverage: Solar panels typically come with warranties that cover defects in materials and workmanship, as well as performance guarantees. It is important to understand the terms of the warranty before purchasing solar panels. The warranty can provide protection against unexpected repairs or replacements.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
-
How much did the homeowner initially invest in solar panels? The article does not specify the exact amount the homeowner invested in solar panels. Solar panel installation costs can vary greatly, usually ranging from $15,000 to $25,000 or more, depending on system size and installation factors.
-
What is net metering, and how does it benefit solar panel owners? Net metering is a policy that allows homeowners to receive credit on their electricity bill for any excess electricity their solar panels send back to the grid. This results in credits on their energy bill or even cash payments.
-
Besides reduced energy bills, what other financial benefits are associated with solar panel installation? Besides reduced energy bills, homeowners may also benefit from federal and state tax credits, rebates, and increased property value.
-
What are some factors that can affect the performance of solar panels? Factors such as the amount of sunlight, orientation and angle of the panels, weather conditions, panel technology, and shading can all affect the performance of solar panels.
-
How long do solar panels typically last, and what maintenance do they require? Solar panels typically last 25 to 30 years and require minimal maintenance. Cleaning the panels periodically to remove dirt and debris is generally sufficient. The inverter, which converts DC to AC electricity, may need to be replaced after 10 to 15 years.